Recently, the team of Professor Zhong Wenying and Associate Professor Xu Bo of CPU School of Science published the latest research results in Journal of Materials Chemistry A (Impact Factor: 11.301), a leading journal in the field of materials science of the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC), reporting two-dimensional (2D) quinazoline based covalent organic framework as a potential candidate for solar cells. Associate Professor Xu Bo is the first author. Professor Zhong Wenying and Associate Professor Xu Bo are the co-corresponding authors of this article.
At present, the team of Zhong Wenying and Xu Bo has made great progress in the field of the applications of two dimensional materials for energy. In this work, the researchers proposed 2D quinazoline based covalent organic framework as a potential candidate for solar cells for its desired direct band-gap (1.18 eV), and promising optical absorption (105 cm-1 ) in the visible and near-infrared light region. They found that Q-COF and ZnSe monolayers could form a heterojunction with a type-II band alignment, using which a photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) of 16.89% can be reached. Under strain engineering, the band gap and the band offset of the Q-COF/ZnSe heterojunction can be effectively tuned, and the PCE can be further improved to 22.32%. This value is even comparable to those of polycrystalline CdTe thin films (21.5%) and perovskites (22.1%). The results show that Q-COF monolayer is an ideal photovoltaic material with high efficiency.
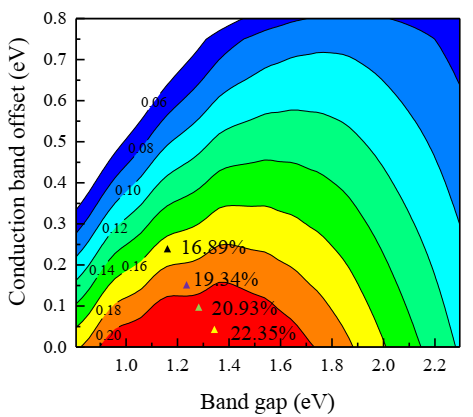
Photoelectric conversion efficiency (%) of the Q-COF/ZnSe heterojunctions under strains.
The research work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 51672126), Young Teachers' Research Funding from College of Science, China Pharmaceutical University (2018CSYT002) and “Double FirstClass” University Project (CPU2018GY25).